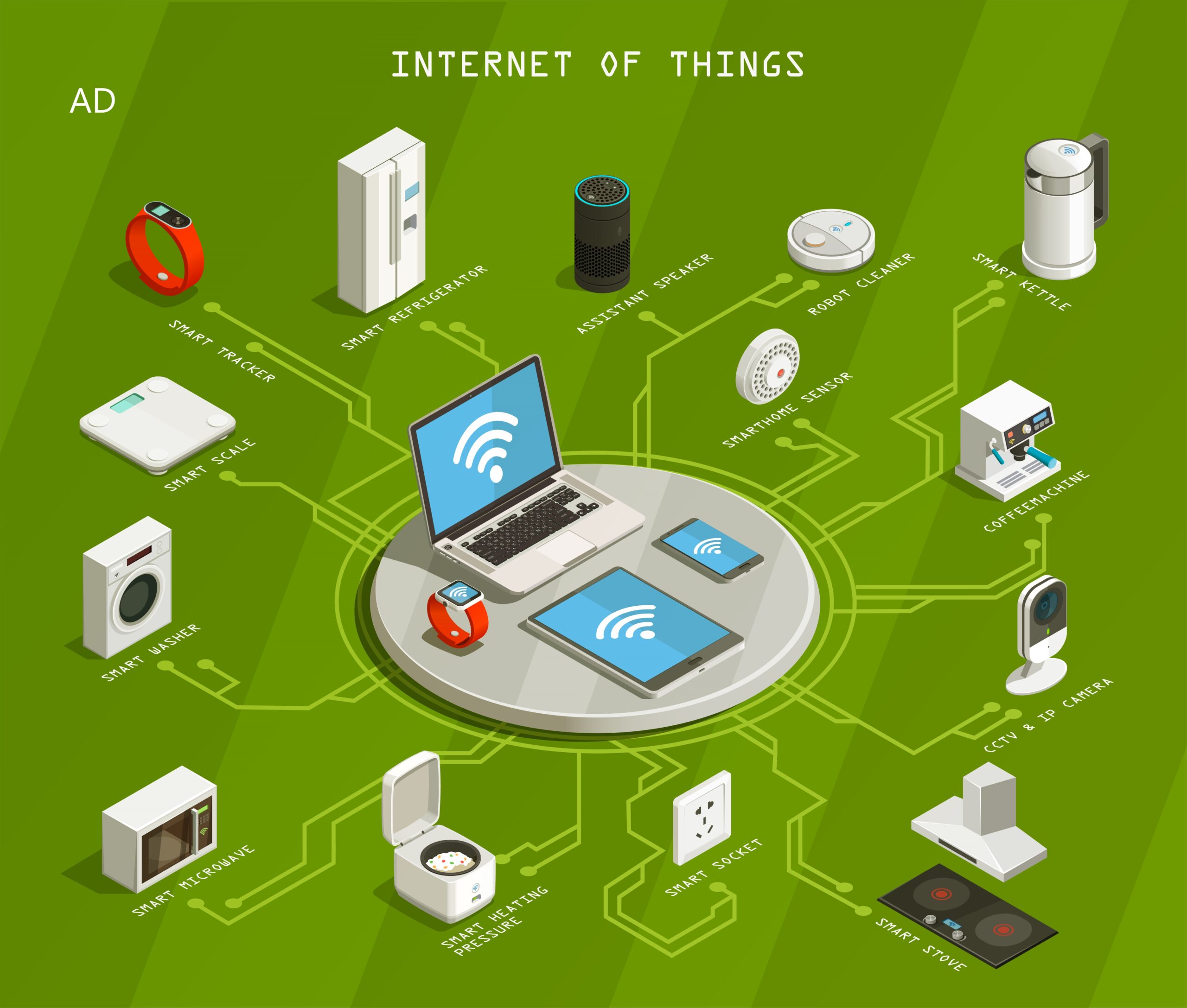
The Internet of Things (IoT) has emerged as a revolutionary force in the world of technology, transforming the way we interact with devices and our surrounding environment. This interconnected network of physical objects and digital systems has paved the way for a new era of innovation and convenience. In this blog, we will delve into the fascinating world of IoT, exploring its applications across various industries and discussing how it has revolutionized our lives.
Features of IOT
Understanding IoT: IoT refers to a network of physical devices, vehicles, appliances, and other objects embedded with sensors, software, and connectivity, enabling them to collect and exchange data over the internet. These devices can communicate with one another, perform tasks, and even make intelligent decisions based on the data they gather.
Smart Homes and Connected Living: One of the most significant applications of IoT is in the realm of smart homes. IoT-enabled devices such as smart thermostats, lighting systems, and security cameras allow homeowners to control and monitor their homes remotely. With voice assistants like Amazon Alexa and Google Home, users can easily control various aspects of their homes using simple voice command.
Industrial IoT and Industry 4.0: IoT has also made a significant impact on industries, giving rise to the concept of Industry 4.0. Industrial IoT allows for seamless connectivity and communication between machines, enabling real-time data monitoring, predictive maintenance, and improved efficiency. IoT sensors can monitor equipment performance, detect faults, and automatically trigger maintenance requests, reducing downtime and optimizing production processes.
Healthcare and Wearable Devices: IoT has transformed the healthcare sector by introducing wearable devices that monitor vital signs, track physical activity, and assist in remote patient monitoring. These devices, such as smartwatches and fitness trackers, enable individuals to take control of their health and provide healthcare professionals with valuable data for diagnosis and treatment.
Transportation and Smart Cities: IoT plays a crucial role in enhancing transportation systems and building smart cities. Connected vehicles equipped with IoT sensors can communicate with traffic signals, parking systems, and other vehicles, optimizing traffic flow and reducing congestion. Furthermore, IoT-enabled sensors and monitoring systems in smart cities can improve energy efficiency, waste management, and public safety.
Agriculture and Precision Farming: IoT has found its way into the agriculture industry, revolutionizing traditional farming practices. Smart farming techniques leverage IoT devices to monitor soil conditions, weather patterns, and crop health. This real-time data helps farmers make informed decisions about irrigation, fertilizer application, and pest control, leading to increased crop yields and resource efficiency.
Retail and Inventory Management: IoT has significantly impacted the retail sector by improving inventory management and enhancing the customer experience. Smart shelves and RFID tags enable retailers to track inventory levels, monitor product expiration dates, and optimize restocking processes. IoT-based beacons and sensors also provide personalized offers and recommendations to customers based on their location and preferences.
Environmental Monitoring and Sustainability: IoT has the potential to address pressing environmental challenges. Connected sensors can monitor air and water quality, detect leaks and waste, and enable efficient energy management. By collecting and analyzing vast amounts of data, IoT can help in creating sustainable solutions and reducing the ecological footprint.
Technical Aspect of IOT
Sensors and Actuators: Sensors are devices that collect data from the physical environment. They can measure various parameters such as temperature, humidity, light intensity, motion, and more. Actuators, on the other hand, are devices that can control or manipulate physical objects based on the received data, such as turning on/off a switch or adjusting a motor’s speed.
Connectivity: Connectivity is a crucial aspect of IoT. It allows devices to communicate and exchange data over the internet or other networks. IoT devices can utilize various communication technologies, including Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, cellular networks (3G, 4G, 5G), and low-power wide area networks (LPWAN) like LoRaWAN or NB-IoT.
Protocols: IoT devices use communication protocols to establish standardized rules for data transmission. Common protocols include MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport), CoAP (Constrained Application Protocol), HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol), and WebSocket. These protocols ensure efficient and secure data exchange between devices and servers.
Cloud Computing: Cloud computing plays a vital role in IoT by providing storage, processing power, and scalability. IoT devices can send their data to cloud servers for storage, analysis, and further processing. Cloud platforms also offer services like real-time data streaming, machine learning, and data analytics, enabling advanced insights and decision-making.
Edge Computing: Edge computing brings computational capabilities closer to IoT devices, reducing latency and enhancing real-time processing. Edge devices, such as gateways or edge servers, can perform data preprocessing, filtering, and analysis locally, without relying heavily on cloud infrastructure. This approach improves response times, security, and reduces the amount of data sent to the cloud.
Data Analytics and Artificial Intelligence: IoT generates massive amounts of data. To extract meaningful insights, data analytics and artificial intelligence (AI) techniques are employed. AI algorithms can analyze IoT data, identify patterns, make predictions, and enable autonomous decision-making. This enables applications like predictive maintenance, anomaly detection, and intelligent automation.
Security: Security is a critical aspect of IoT due to the interconnected nature of devices and the sensitivity of the data being transmitted. Robust security measures, including encryption, authentication, and access control, are implemented to protect IoT devices and data from unauthorized access, manipulation, or cyber-attacks.
User Interfaces: IoT devices often have user interfaces that allow users to interact with them. These interfaces can be through mobile apps, web portals, or dedicated control panels. User interfaces provide a convenient way for users to monitor and control IoT devices, access data, and customize settings.
Conclusion
The Internet of Things has ushered in a new era of connectivity, where everyday objects and systems seamlessly interact with each other. From smart homes to industrial automation, healthcare to transportation, and agriculture to retail, IoT has permeated various aspects of our lives, making them more efficient, convenient, and interconnected. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect IoT to play an even more significant role in shaping the future, enabling us to create smarter, sustainable, and connected societies.